In networking, the mode of transmission refers to the way data is transferred between devices in a network. There are two primary modes of transmission: simplex and duplex.
Simplex Mode: 📤

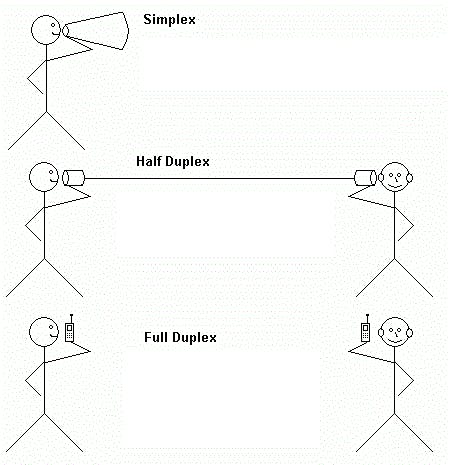
In simplex mode, data can only flow in one direction, from the sender to the receiver.
Example: Television broadcasting. TV stations transmit signals to viewers, but viewers cannot send signals back through the same channel.
Half-Duplex Mode: 🔄
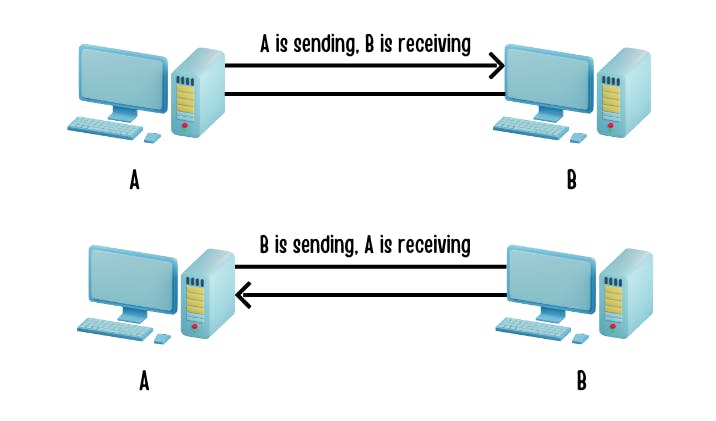
In half-duplex mode, data can flow in both directions, but not simultaneously. Communication alternates between sending and receiving.
Example: Walkie-talkies. Users can either talk or listen, but not both at the same time.
Full-Duplex Mode: 🔄🔄
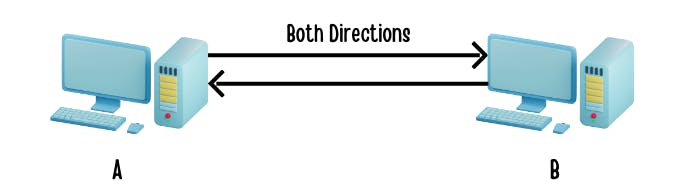
In full-duplex mode, data can flow in both directions simultaneously, allowing for real-time communication.
Example: Telephone conversations. Both parties can speak and listen at the same time, enabling a natural and continuous exchange of information.
Understanding the mode of transmission is crucial for designing efficient and effective communication systems, ensuring that devices can communicate seamlessly based on the specific requirements of the network. 🌐
